Related Thermal Management Blog Articles
Digital and Physical: Thermal Twins for Developing Thermal Management Solutions
As we all know, finding thermal management solutions is becoming an increasingly critical but also an ever more challenging issue for the semiconductor industry...
Read MoreThermal Test Chips (TTCs) for Advanced Semiconductor Packaging
Thermal management is becoming an ever more critical challenge for semiconductor devices, as the functional density and power density increase – especially with advanced packaging. Thermal test chips (TTC) are a critical enabler for developing thermal management solutions for high-power semiconductor devices...
Read MoreSo You Want to be in Manufacturing?
"So You Want to be in Manufacturing?" Blog post for young manufacturing engineers, technicians, and manufacturing operations professionals.
Read MoreAdvanced Technology Workshop on Thermal Management
Indium Corporation presents paper at Advanced Technology Workshop that provdes metal thermal interface materials (TIMs) have a higher insertion rate and higher thermal conductivity than traditional TIMs for burn-in and test.
Read MoreWhat Makes a Good Thermal Interface Material?
There are many considerations that can figure into your thermal interface material selection.
Read MoreAll of our thermal interface materials are metal-based, which means they have a very high conductivity as compared to polymer-based thermal interface materials.
Indium metal, for example, has a conductivity of 86W/mK and is 4 times softer than lead. It's ductility and thermal conductivity make it ideal as a compressible thermal interface material. For the thermal K values of other thermally conductive materials, check out our thermal K list.
Metal TIMs can be divided into two categories:
- Solder TIMs that reflow and melt to form a mechanical bond
- Compressible TIMs that serve as gap fillers and do not need heat to form a bond
Compressible (or non-reflow) TIMs include:
Solder interconnects can also act as a thermal interface.
Indium Corporation makes over 200 different alloys for solder preforms. These alloys can be pure indium, indium alloys, Pb-free, or Pb-contained. Please consult one of our technical support engineers to identify the best metal TIM for your application.
Solder TIMs include:
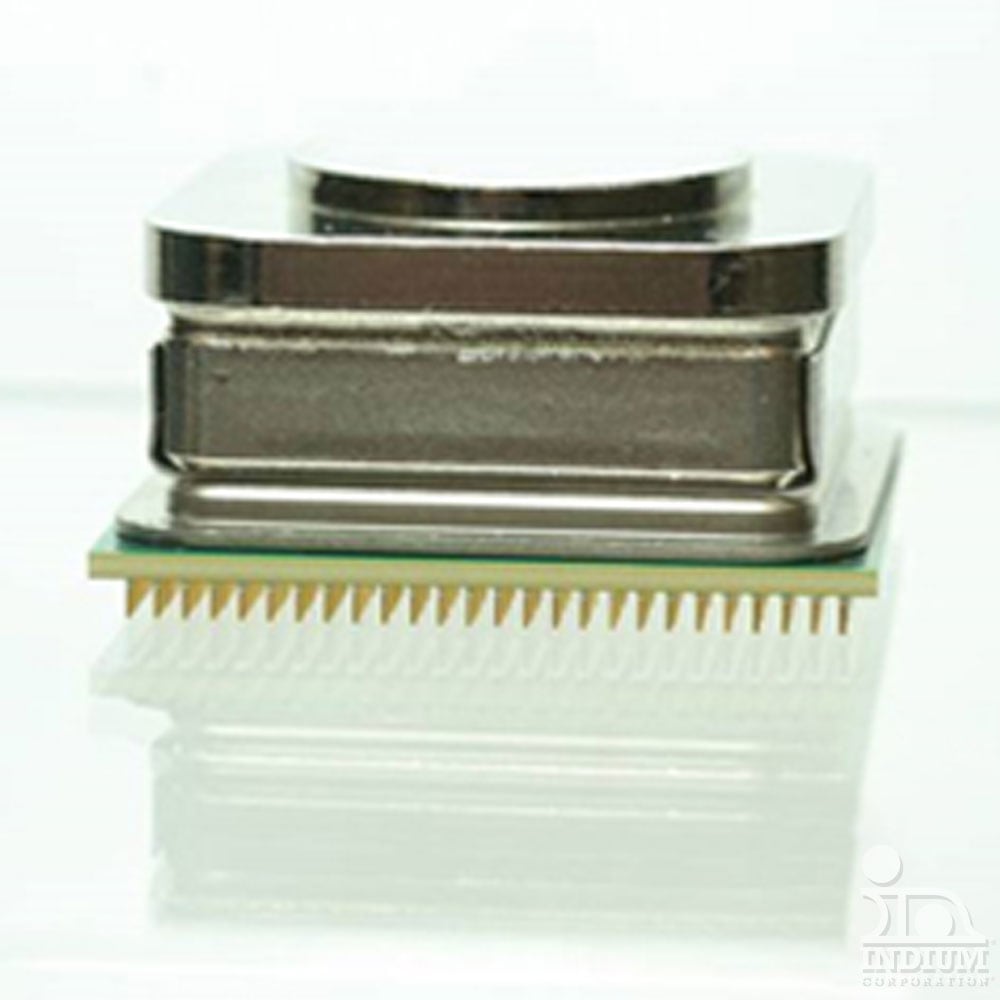
Power Semiconductor
Indium Corporation manufactures die-attach solder paste for vacuum soldering. Indium Corporation's IGBT die-attach solder paste can be screen printed or stencil printed and is easy to clean.
Indium Corporation also provides solder ribbon and solder preforms for die-attach applications. Tape & reel packaging allows preforms to be advanced and placed with speed and accuracy. Semiconductor-grade ribbon and preforms come in ultra-pure alloys and adaptable packaging, such as tape & reel, custom spools, and cartridge packs, to increase productivity, performance, and efficiencies.
All material is recyclable and reclaimable.
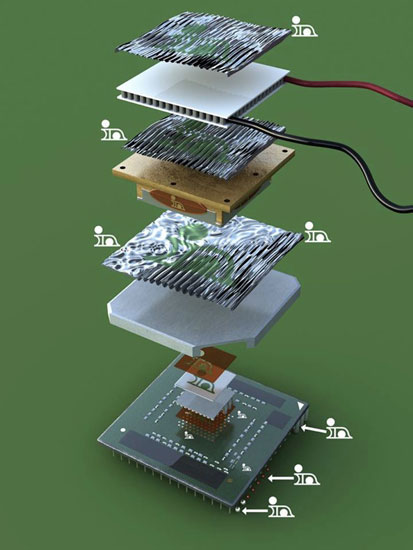
TIM1, TIM1.5, TIM2
Indium Corporation continues to lead the way in developing cutting-edge thermal interface materials (TIMs) and processes, including applications for TIM1, TIM1.5, and TIM2.
- TIM1: Solder preforms are used as a solder thermal interface material between a processor die and a heat-spreader at the TIM1 level.
- TIM1.5: In mobile applications or bare die applications, such as laptops or video graphics boards, there is no heat-spreader. Instead, the die is in direct contact with the cooling solution. That is why we call this thermal interface level TIM1.5. Here we recommend our compressible thermal materials, such as Heat-Springs® or liquid metal
- TIM2: In the TIM2 level between the heat-spreader and the heat-sink we also recommend our compressible interface material - Heat-Springs® or liquid metal
Thermal K Values List
![]() Denotes Materials that Indium Corporation can provide
Denotes Materials that Indium Corporation can provide
| Indalloy® Number | Material | Thermal Conductivity W/(m - K) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond | 1300-2400 | ||
| Pure Silver | 429 | ||
| 200 | 100Au | 318 | |
| Pure Aluminium | 240 | ||
| 4 | Pure Indium | 86 | |
| 290 | 97In3Ag | 73 | |
| 128 | 100Sn | 73 | |
| 3 | 90In10Ag | 67 | |
| 201 | 91Sn9Zn | 61 | |
| 182 | 80Au20Sn | 57 | |
| 227 | 77.2Sn20In2.8Ag | 54 | |
| 106 | 63SnPb37 | 50 | |
| 9 | 70Sn18Pb12In | 45 | |
| 2 | 80In15Pb5Ag | 43 | |
| 204 | 70In30Pb | 41 | |
| 1E | 52In48Sn | 34 | |
| 1 | 50In50Sn | 34 | |
| 121 | 96.5Sn3.5Ag | 33 | |
| 205 | 60In40Pb | 29 | |
| 205 | 60In40Pb | 29 | |
| 133 | 95Sn5Sb | 27 | |
| 281 | 58Bi42Sn | 19 | |
| 19 | 51In32.5Bi16.5Sn | ||
| 51 | 62.5Ga21.5In16Sn | 40 | |
| Phase Change Materials | 3 - 8 | ||
| Thermal Grease | .75 - 6 | ||
| Ag - Filled Die Attach | 1.3 - 5 | ||
| Molding Compounds | 0.6 - 0.7 | ||
| BT Epoxy | 0.19 | ||
| FR - 4 | 0.11 |


