Related Solder Paste Videos
Related Solder Paste Blog Articles
Au-mazing Solutions: How AuLTRA® MediPro is Setting the Gold Standard for Medical Device Soldering
Indium Corporation's AuLTRA® MediPro product line offers high-performance gold-based solder materials for medical devices, ensuring reliability and precision in critical applications like pacemakers, hearing aids, and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM). With properties such as superior oxidation and corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and hermetic sealing, AuLTRA® MediPro guarantees long-lasting connections in wearable, implantable, and industrial devices. This complete range of materials, including paste, wire, preforms, and ribbon, upholds the "Gold Standard" in medical technology, certifying quality, safety, and dependability.
Read MoreRosin 101: The Critical Role of Rosin in Solder Paste Formulation and Enhancing Electronics Assembly Process Efficiency
A key ingredient that is critical to the solder paste formulation is rosin, which plays a significant role in enhancing the performance of the solder paste and hence providing high process yield.
Read MoreKeep Your Solder Paste Cool!
Recently, I have been receiving many inquiries on the topic of keeping solder paste cool during the heat waves this summer. Here are a few tips to keep in mind when you receive your next batch of solder paste.
Read MoreSolder Paste is Not a Commodity
Folks, I was getting a little cabin fever, so I thought I would go for lunch at Simon Pearce. The ambiance there always relaxes and refreshes me. So, the ma&ic...
Read MoreConclusion to: Profits are Down. Could a Cheaper Solder Paste Have Caused it?
Folks, Let's see how Ivy University grad student Maria Gonzales is handling her assignment to find the lost profits a Liberty Elecronics… Maria...
Read MoreSolder Paste Features & Benefits
Indium Corporation produces a wide range of solder paste products to fit every need and challenge in the PCB Assembly and semiconductor manufacturing market space.
No-clean solder paste is by far the most prevalent solder paste in modern electronic manufacturing, but there is still a purpose and a fit for water-soluble and RMA solder paste as well. Solder paste can be manufactured in hundreds of alloys and with powder size ranging from Type 3 to Type 8. Solder pastes are available for a wide variety of process deposition techniques, including printing, dipping, dispensing, jetting, and pin transfer assembly. Each formula is specifically designed to meet the gamut of manufacturing challenges that plague the electronics manufacturing industry. Whether you are dealing with warpage induced defects, voiding, insufficient solder paste volume, or electrical or mechanical reliability issues, Indium Corporation’s solder pastes – coupled with our world-renowned technical support – allow for the lowest total cost of ownership and fewer end-of-line defects.

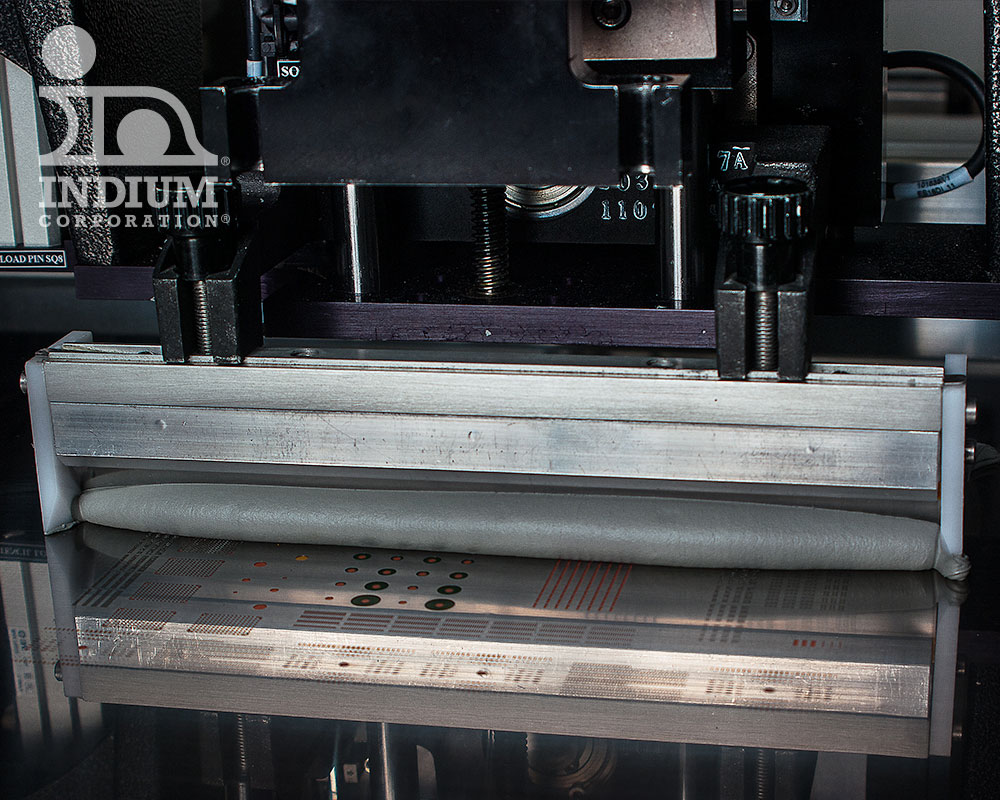
Tin-Lead (SnPb)
Indium Corporation offers a number of SnPb solder pastes for circuit board assembly and high-Pb applications common in semiconductor packaging.
With decades of proven flux technology, these solder pastes will provide you with the highest end-of-line yields.
| No-Clean | |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Value Proposition |
| Indium8.9HF | Best all-around halogen-free paste |
| Indium8.9ES | Excellent print transfer efficiency for the broadest range of processes |
| NC-SMQ92H | Modified version of NC-SMQ92J that maximizes print performance |
| NC-SMQ92J | Industry-leading solder paste with a soft residue that reduces false failures at ICT |
| NC-SMQ51SC | Exceptional stencil life and tack strength, and consistent print definition in ultra-fine pitch applications |
| NC-SMQ80 | Specialty solder paste (InPb) for soldering to gold surfaces |
| Water-Soluble | |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Value Proposition |
| Indium6.6HF | Superior wetting to a variety of surface finishes and exhibits the best voiding performance |
| Indium6.4R | A versatile, low-voiding solder paste (InPb) |
| Indium6.3 | A low voiding solder paste with a wide reflow window |
| RMA | |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Value Proposition |
| RMA-155 | Low voiding solder paste with a wide reflow window |
| RMA-SMQ51AC | A no-clean RMA solder paste with excellent soldering performance |
Package-on-Package Paste
Package-on-package (PoP) assembly is most commonly carried out by printing solder paste onto the substrate and then placing the logic chip into the paste. The memory package is then dipped into a PoP solder paste or flux, placed on top of the logic chip, and then reflowed. This is generally a no-clean process. PoP flux is most commonly used, rather than PoP solder paste, because of the ease in setup and maintenance. PoP solder paste is a bit more challenging to set-up and maintain because of the possibility of bridging, but it will help with components that warp. PoP flux will not accommodate for component warpage.
| Product | Value Proposition |
|---|---|
| PoP Paste Indium9.88HF | A halogen-free material designed for use in 0.4mm pitch and larger PoP applications. Has a rheology designed to provide a maximum amount of solder paste on the package bumps to accommodate for component warpage. Compatible with Sn/Pb and SAC solder alloys. |
| PoP Flux 89HF-LV | Halogen-free industry leading PoP Flux. Optimized for Pb-free and Sn/Pb applications. |
| PoP Flux 89HFLV-B | A blue/black version of PoP Flux 89HF-LV for automated flux presence inspection using the pick and place vision systems. |

Solder Fortification® Preforms
Obtaining the precise amount of solder to ensure a stronger solder joint is critical in electronics manufacturing. However, miniaturization trends, such as the reduction of stencil thickness and more tightly fitted components, make this increasingly difficult. Solder Fortification® Preforms can provide the solution for these challenging issues.
Solder Fortification® Preforms are rectangular shaped pieces of alloyed metal that do not contain any flux. The preform is added to a deposit of solder paste using standard pick and place equipment. Since the alloy for both the preform and the solder paste are the same, the preform will reflow at the same temperature as the solder paste, with the solder paste providing the necessary flux. The preform increases the volume of solder above what could be achieved with just solder paste, especially for applications using stencils with a pitch of 0.3mm or less.
Advantages
The advantages of Solder Fortification® Preforms include:
- Stronger solder joints, which help improve drop test results
- Increased solder volume compared to what could be achieved with just solder paste
- Fewer issues with flux residue as the solder-to-flux ratio is increased
- Reduced rework and other manual processes to add solder volume
- Elimination of costly or time-consuming processes, such as wave soldering or selective soldering
- Improved shape and volume of fillet to ensure joints meet IPC specifications
Solder Fortification® Solution Options
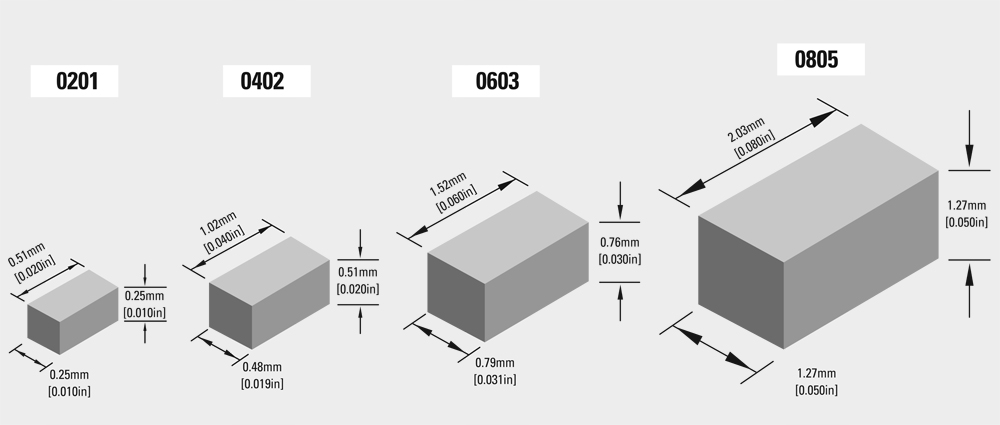
| Quantity Per Reel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Size | Quantity Per Reel 7" |
Quantity Per Reel 13" |
Example Weight: SAC305 (grams/ea) |
| 0201 | .010" x .020" x .010" (0.254mm x 0.508mm x 0.254mm) |
1k | 50k | 0.00024 |
| 0402 | .020" x .040" x .020" (0.508mm x 1.01mm x 0.48mm) |
1k | 15k | 0.00182 |
| 0603 | .030" x .060" x .030" (0.76mm x 1.52mm x 0.787mm) |
1k | 15k | 0.00672 |
| 0805 | .050" x .080" x .050" (1.27mm x 2.03mm x 1.27mm) |
1k | 15k | 0.02410 |
Solder Fortification® Design Guide
Email Us Your Solder Fortification® Question
Packaging
Solder Fortification® Preforms are packaged in tape & reel for easy placement by standard pick and place machines. For more information on Solder Fortification® Preform packaging, download the design guide below.
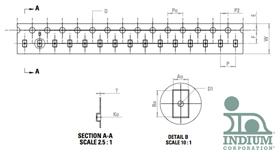
Alloys
Solder Fortification® Preforms are available to deliver a precise amount of solder in virtually any alloy to correspond to the alloy in the solder paste.
Common alloys include:
- SAC305 and SAC387
- Sn63 and Sn62
- BiSn and BiSnAg
Technical and Customer Support
Selecting the right solder alloy, form, and dimensions are key to producing a quality end product. Indium Corporation can provide a wide variety of alloys, prototype to production quantities and optimized packaging for your specific application.
Our engineers offer:
- A thorough understanding of each customer’s needs and applications
- A seasoned problem-solving attitude
- Knowledge of manufacturing processes and materials handling requirements
- Expertise in metal fabrication, product packaging, and customer satisfaction
Try our new Process Optimization Calculators and then contact our technical support engineers to discuss how to improve your results.

Gold-Based Solder Paste
Gold-tin solder paste is used in a variety of high-reliability applications, where its high melting point, non-creep, high-tensile stress, thermal and electrical conductivity, as well as proven usage life makes it a standard "known-good" material.
Advantages
- Highest tensile strength of any solder
- High melting point is compatible with subsequent reflow processes
- Pb-free
- Superior thermal conductivity
- Resistance to corrosion
- Superior thermal fatigue resistance
- Good joint strength
- Excellent wetting properties
- Resistance to oxidation
- AuSn is compatible with precious metals
- AuSn is RoHS compliant
Gold-tin Solder Paste
- 80Au/20Sn Powder
- Type 3 (25-45 microns)
- Type 4 (15-38 microns)
- Type 5 (15-25 microns)
- Type 6 (10-20 microns)
- Type 6 SGS (5-15 microns)
- Type 7 SGS (2-11 microns)
- Top performing formulations:
- AuLTRA5.1 (used in high-power LED and MEMS)
- AuLTRA5.1LS (for difficult to solder surfaces in die-attach)
- AuLTRA3.2 (excellent for use in high-power LED module arrays)
- Low-volume packaging
- Jars (10g per jar)
- Syringes (5cc syringes)
Alternative Methods of Using AuSn
| Characteristics | Solder Paste | Solder Preform | Evaporation | Alloy Plating | Plating by Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum bondline thickness | 25.00μm | 12.00μm | 0.01μm | 0.25μm | 2.50μm |
| Cleanliness | Low cleanliness (flux surface contamination) | High cleanliness (when no flux used) | High cleanliness | Good cleanliness (trace of organic impurities only) | Good cleanliness (organic co-deposit impurities) |
| Deposition equipment | Stencil printer or dispenser | Manual or pick & place | Evaporation chamber | Plating line | Plating line |
| Device heat exposure | >280°C | >280°C | >Ambient | Ambient | Ambient + diffusion heating step |
| Strengths | Low-cost equipment; manual or automated assembly; rapid deposition rate | High purity; manual or automated assembly; preforms designed to match deposition footprint | Very high purity; rapid deposition; low-cost equipment; thin to thick layers | Good purity; deposition targeted to conducting surfaces | Good purity; deposition targeted to conducting surfaces |
| Weaknesses | Flux residue inclusion; thick deposits only; requires diffusion step; requires cleaning; refrigerated storage | Expensive automation equipment; thick depositions only; accurate manual placement difficult, may require flux or reducing atmosphere | Wide area deposition (material loss); may require diffusion step | Expensive equipment; difficult to control composition; low deposition rates | Expensive equipment; difficult to control composition; low deposition rates; requires diffusion step |
Factors to consider
- Higher yields and cost per unit make gold a viable option, even though the initial cost is higher than alternative solders
- A low oxygen atmosphere may be required if the application is flux free
- Some applications require pressure to promote good, void-free reflow on horizontal surfaces.
- In step soldering or processes that may require rework, soldering to gold plated surfaces results in an intermetallic that melts at a higher temperature than the original alloy. When using the AuSn alloy, this can be addressed by using high tin-containing alloys.
- Alternative methods, such as scrubbing, forming gas or formic acid, may be needed for oxide removal of the soldered surface.
Processing Options
- Vacuum soldering: flux-less and void-free soldering
- Die-attach: high process temperature
- Reflow: convection, infrared, and induction
- Laser soldering: targeted soldering
- Vapor phase reflow: uniform heating
- Manual Soldering: solder iron, hot plate, ultra sonic, and dipping

Jetting and Microdispensing Solder Paste
Jetting and microdispensing solder pastes are specifically formulated for fine-pitch and ultra-fine dispensing/jetting for various applications. Indium Corporation’s jetting and microdispensing pastes provide reliable dispensing of consistent size deposits in automated dispensing or jetting equipment.
Jetting or microdispense solder pastes include no-clean and water-soluble solder pastes, and are used with SnAgCu and SnPb alloy systems. It is important that they ONLY be used with the matched printable solder pastes. These products are designed for reflow in air or nitrogen atmosphere of 100ppm oxygen or less.
Process Optimization Calculators
Try our new Process Optimization Calculators and then contact our technical support engineers to discuss how to improve your results.
Technical Support
Contact our technical support engineers to help determine the best solder powder and paste for your application.