Applications
Low Temperature Liquid & Fusible Alloys
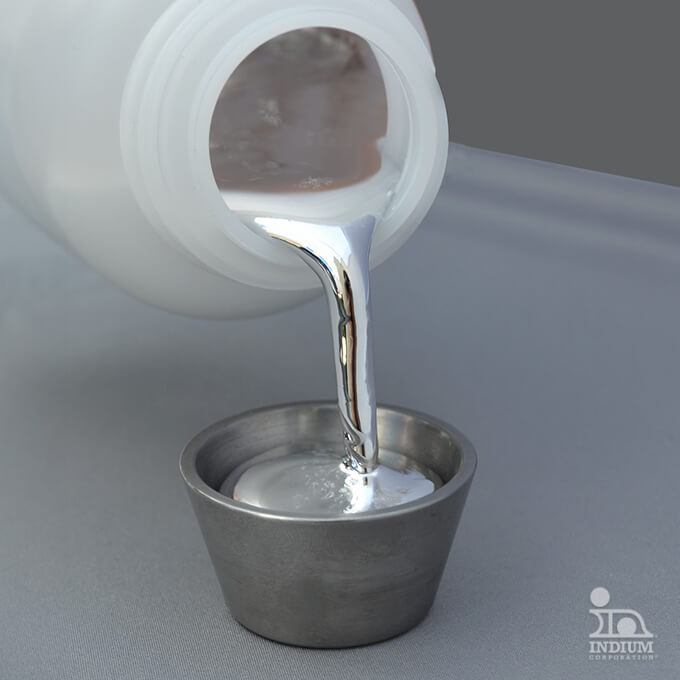
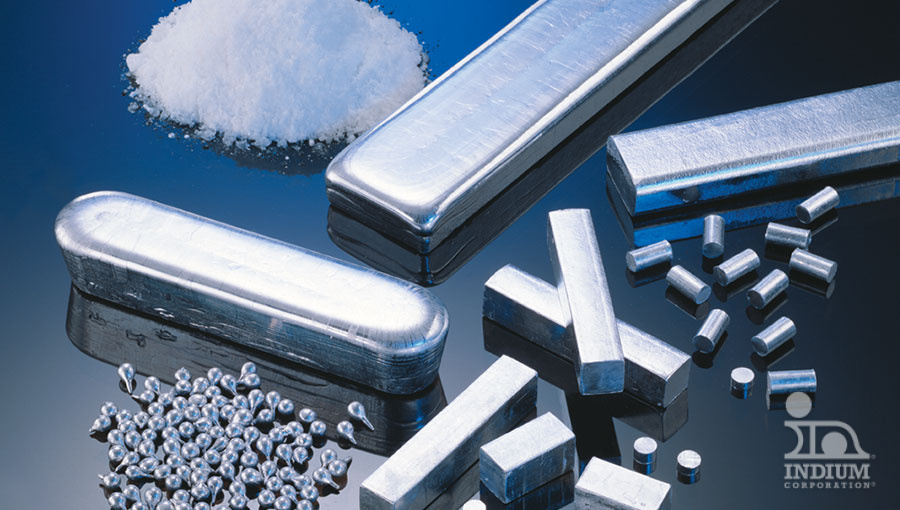
Creating alloys by mixing elemental metals allows to achieve melting points that are not obtainable with single element metals. The specific melt point ranges that can be obtained make these materials attractive for a range of applications across a group of industries.

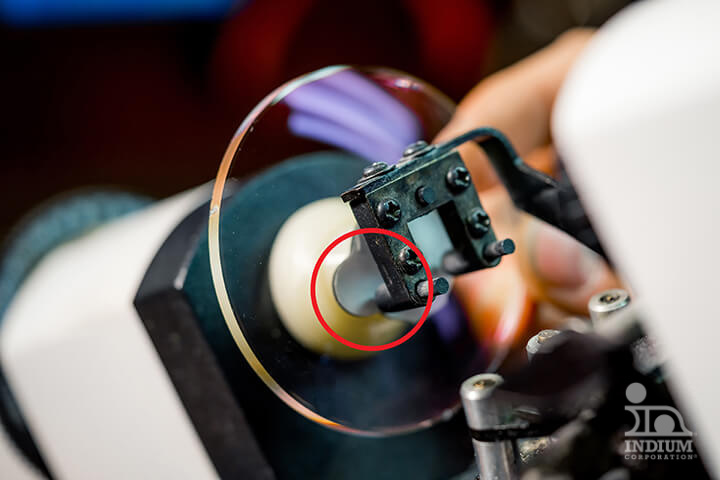
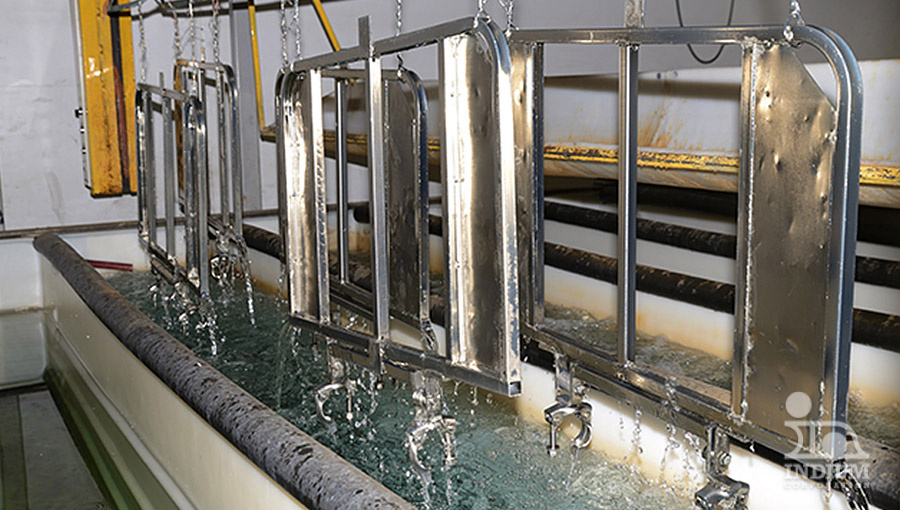
Lens-blocking
Overview
Alloys that melt at relatively low temperatures enable a large range of uses.
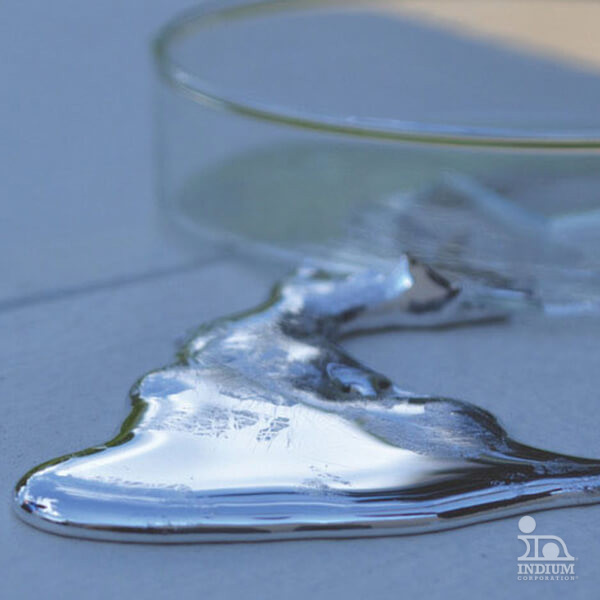
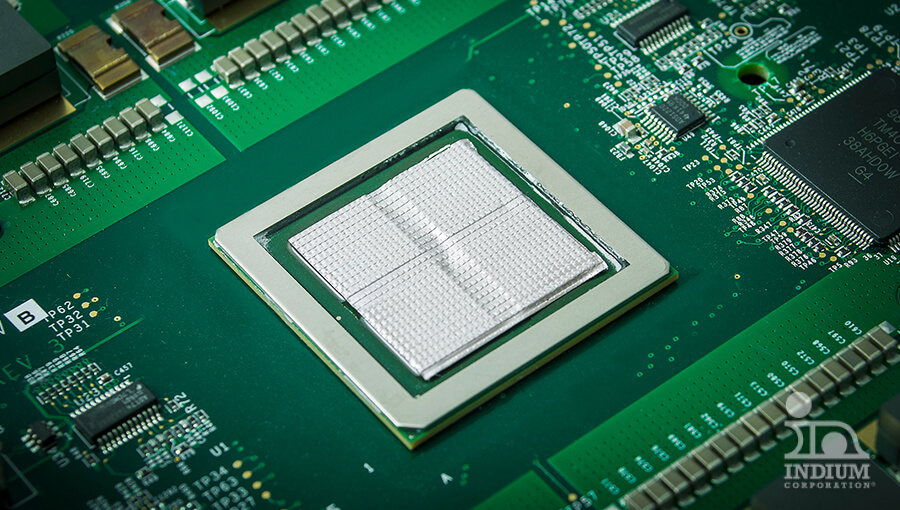
Gallium, which melts near room temperature, can have its melting point further reduced by alloying with indium and tin. These liquid metals are vital for thermal management, efficiently conducting heat away from CPUs, GPUs, and other high-power semiconductor chips in AI and data center applications.
Above 50°C, fusible alloys serve as essential temporary work-holding materials, easily melting to clamp and protect workpieces during finishing operations like lens-blocking and turbine blade finishing. Additionally, the melting phase change of these alloys can trigger fire sprinklers, providing a fail-safe, passive system that operates without electricity.
Benefits
Select from a large variety of alloys to control the performance of your application at a precise melting point
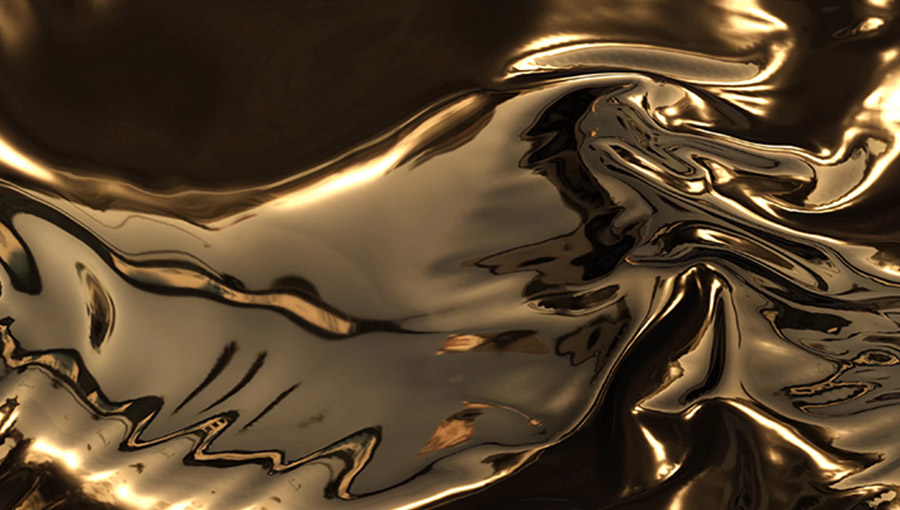
Liquid Metals at or Below Room Temperature
Gallium-based liquid metals ideal for various applications.
Precise Melt Point Control
Customize melt points ranging from 46°C to 200°C with specific alloys.
Sharp Melt Point with Eutectic Alloys
Achieve precise and consistent melting behavior with eutectic compositions.
Wide Range of Compositions
Choose from a variety of alloys, including Pb- and Cd-free options for safety and environmental compliance.
Related Applications
Related Markets
Your Success
is Our Goal
Optimize your processes with the latest materials, technology, and expert application support. It all starts by connecting with our team.