Applications
Low-Temperature Soldering
Low-temperature soldering has surged in popularity, driven by increasing technical and manufacturing challenges and a strong emphasis on sustainability. The industry is increasingly focused on developing alloys and processes tailored to diverse low-temperature needs. At Indium Corporation, we’re transforming the electronics manufacturing landscape with our innovative suite of low-temperature soldering materials and decades of expertise in low-temperate applications.

Overview
Enhancing Performance with Sustainable Solutions
Low-temperature soldering offers both technical and environmental benefits. It helps reduce thermal stress, advance technology for complex designs, and eliminate heat-induced defects like warpages or damage to sensitive components. At the same time, it lowers energy costs and reduces carbon emissions, aligning with environmental regulations and supporting our customers’ sustainability goals.
Low-Temperature Soldering Applications
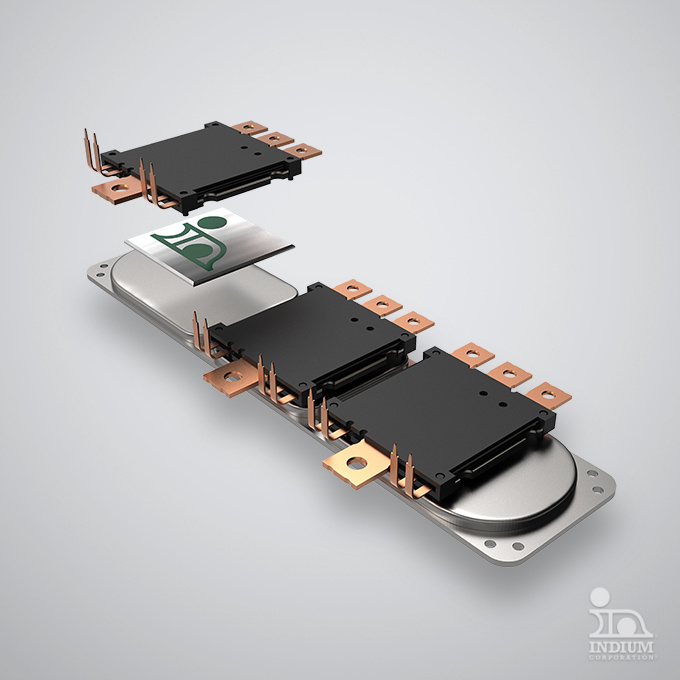
Attachment to Circuit Boards
Attachment of temperature-sensitive components to printed circuit boards.
Step Soldering
Step soldering, when a secondary, lower temperature reflow process is required after a standard SAC soldering process is completed.
Eliminate Warpage
Eliminating warpage of thinner chips due to high-temperature reflow.
IoT Devices
Low melting or low-Tg flex circuitry which are used in cellphones, smartwatches, and many internet-of-things (IoT) devices.
Large Area Array Devices
Large area array devices – such as BGAs – to avoid head-in-pillow (HIP) and non-wet-open (NWO) failures.
Low-Temperature Soldering Products
Discover our diverse portfolio of solders, including traditional indium- and bismuth-based alloys, as well as the innovative Bi+ and Durafuse® LT series, designed to meet advanced requirements.
Related Applications
Related Markets
Our low-temperature soldering solutions are used in a wide range of industries, including mobile, server, automotive, infrastructure, and more. We work closely with our customers to provide tailored solutions for their unique applications.
Mastering Solder Preform Technology With Low Temperature Solder Alloy Solutions
Achieving efficiency, reliability, and exceptional thermal performance is crucial in package-attach soldering applications for power modules. However, the high reflow temperatures required by
Back to the Basics: Flux
During my first few weeks as a Technical Support Engineer at Indium Corporation, Iresearched extensively and consulted with my team to find out when flux should be used and why it’s essential
Durafuse®LT Solves a Too-High Reflow Temperature Concern
Folks, Let's see how Monica and Guy are doing in solving the too-high temperature reflow concern….. Patty was sitting in her office, and, typical to her dynamic personality, was excited and
A Low Temperature Solder Paste with Superior Thermal Cycle and Drop Shock Performance
Folks, Professor Patty Coleman is at it again. Let's listen in….. Monica Reese was conflicted as she sat at her desk. She was excited that Professor Patty Coleman helped her get a job with
Ramp-to-Peak: The First Thought in a Reflow Profile
Folks, I am working on a book with my Indium Corporation colleagues on tackling soldering defects in electronics.It is a follow up to our The Printed Circuits Assembler's Guide to Solder Defects.
Rosin 101: The Critical Role of Rosin in Solder Paste Formulation and Enhancing Electronics Assembly Process Efficiency
“A key ingredient that is critical to the solder paste formulation is rosin, which plays a significant role in enhancing the performance of the solder paste and hence providing high process
Improved IMC Growth Rate Calculator
Folks, Peter writes: Dear Dr. Ron, I amthrilled with your Excel® program to calculate IMC thickness as a function of time. However, I wanted to calculate IMC thickness for times not listed in the
Interconnect Reliability: From the Chip to the System
Interconnect reliability is critical to the reliability of semiconductor packaging and electronic systems. If we look at the life cycle from the chip to the system—from IC design, wafer fab,
Join Me at SMTA PanPac 2024
SMTA PanPac is a unique experience. In addition to the obvious draw of Hawaii in January, the conference tends to host thought leaders in the electronics industry. Along with the expected technical
Your Success
is Our Goal
Optimize your processes with the latest materials, technology, and expert application support. It all starts by connecting with our team.