Flux is a liquid, solid or gaseous material which, when heated, speeds up and/or promotes wetting of the base material(s) by the fluxs removal of any surface oxides on the base material. Flux will protect against further oxidation during the soldering process.
Flux is an important component of most soldering operations. Using the correct flux for the application is essential to insure that a reliable joint is made.
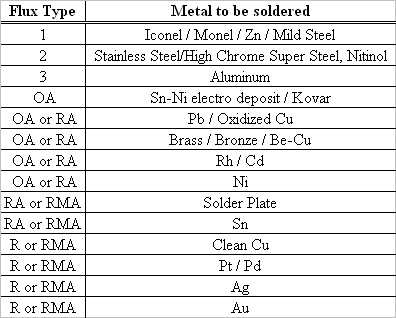
To the right is a chart to help you choose the correct flux type for your application. Most post reflow flux residues need to be removed either to avoid corrosion or for reasons of appearance.
Reducing Gas Atmosphere is a gaseous atmosphere comprised of one or more gases, generally hydrogen and inert filler gas, such as nitrogen. Used where standard fluxes are ineffective at removing and preventing surface oxides.Hydrogen, for example, reduces the oxides, while nitrogen remains inert. It is recommended that both gases be present to effect a fluxing action. About 350°C is best.